The “local device name is already in use” error usually appears when you try to access or reconnect a mapped network drive on a Windows computer. This error message can interrupt your workflow by disconnecting your system from a shared network folder on a file server. When this happens, you may not be able to open, copy, or share files until the issue is resolved. 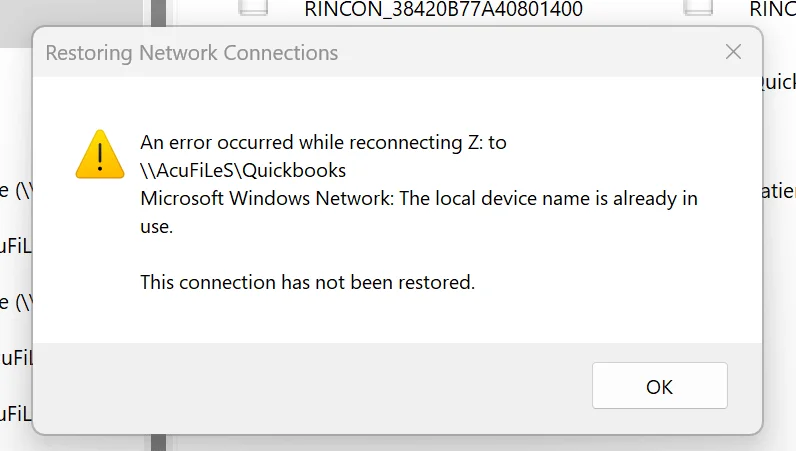
Windows includes a built-in option to map network drives so they show up like regular folders in File Explorer. This makes it easier to reach shared locations without typing network addresses every time. However, even though mapping a network drive is normally simple, Windows can sometimes display this error during the connection process.
This error is fairly common for people who work with networks, including home and office setups. It usually points to a connection conflict or a mismatch between how the drive was mapped and the network you are trying to reach. Fortunately, this issue is well-known and can often be fixed once the underlying cause is understood, which we will explain in this guide.
What Causes the Local Device Name Error on Windows?
This error can show up for more than one reason, and finding the exact cause is not always easy. In many cases, it is linked to drive letters that are already in use or shared settings that are not set the right way. These small conflicts are enough to stop Windows from connecting to a mapped network drive.
Another common reason is low storage space on the network server. When the server does not have enough free space, Windows may fail to connect and show this error.
Connection type conflicts can also trigger this issue. For example, if the network drive was created using a local network and later accessed through a different connection method, Windows may block the link. On top of that, disabled file and printer sharing in Windows Firewall, conflicting drive letters, or damaged network mapping data can all lead to this error appearing on your Windows screen.
11 Ways to Fix “the local device name is already in use” Error on Windows
Disconnect and Remap the Network Drive Using Command Prompt
A good first step is to remove the existing network drive and map it again using Command Prompt.
- Press Windows + S to open search, type Command Prompt, then choose Run as administrator from the menu.

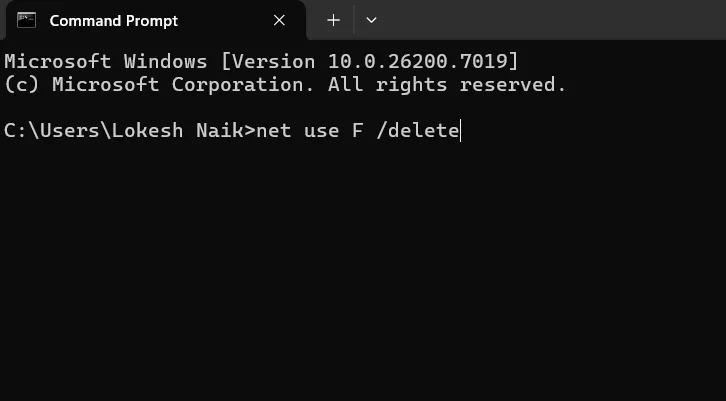
- In the Command Prompt window, type the command net use F /delete and press Enter. (Replace F with the drive letter you want to remove.)

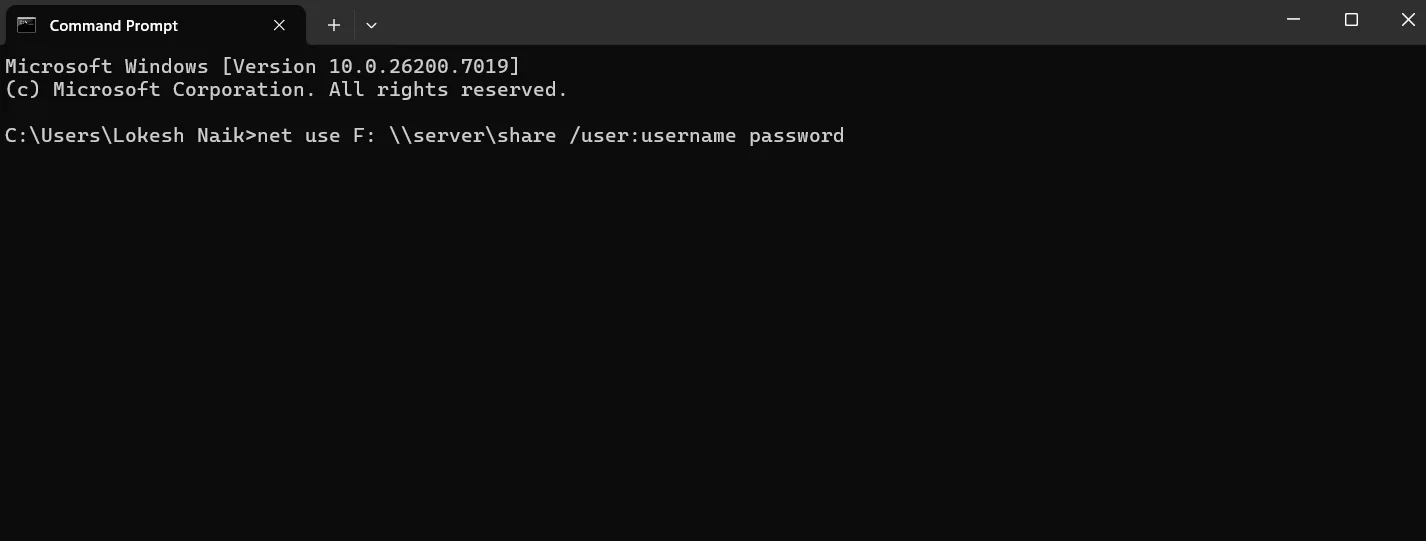
- Once you see a message confirming the drive was deleted, type the command net use F: \\server\share /user:username password and press Enter

- Make sure you change F to the drive letter you want to use. Also, replace username and password with your network login details.
After completing these steps, open File Explorer and check the mapped network drive again. Microsoft also suggests remapping the drive as the main fix for network connection restore errors, so this method is often effective.
Restart the Computer Browser Service
Another useful step is restarting the Computer Browser service. When this service is not working as intended, Windows may fail to keep the network drive connection active and show this error.
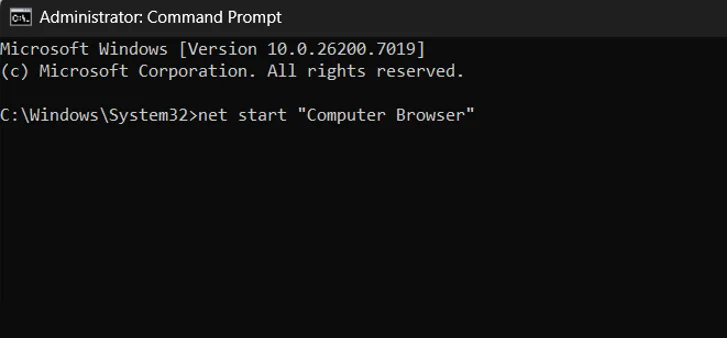
- Press Windows + S, type cmd, then choose Run as administrator.
- When the permission prompt appears, click Yes.
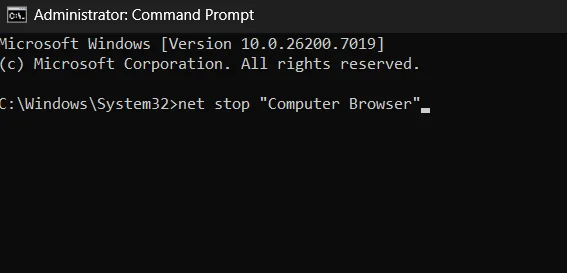
- In the Command Prompt window, type the command net stop “Computer Browser” and press Enter

- After the service stops, type the next command net start “Computer Browser” and press Enter

- Once done, close Command Prompt and check the network drive again to see if the error is gone.
Enable File and Printer Sharing in Windows Firewall
Keeping the firewall turned on is important, but it can sometimes block file and printer sharing on your network. When that happens, Windows may fail to connect to a shared drive and show this error. Turning this option back on usually fixes the issue.
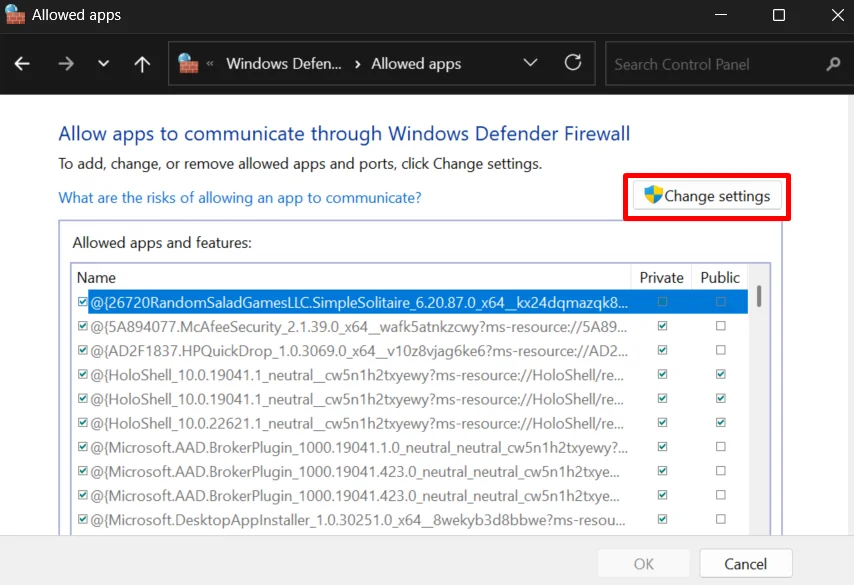
- Press Windows + S, type Control Panel, and open it from the results.
- Click System and Security, then open Windows Defender Firewall.

- From the left side menu, click Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall, then select Change settings.

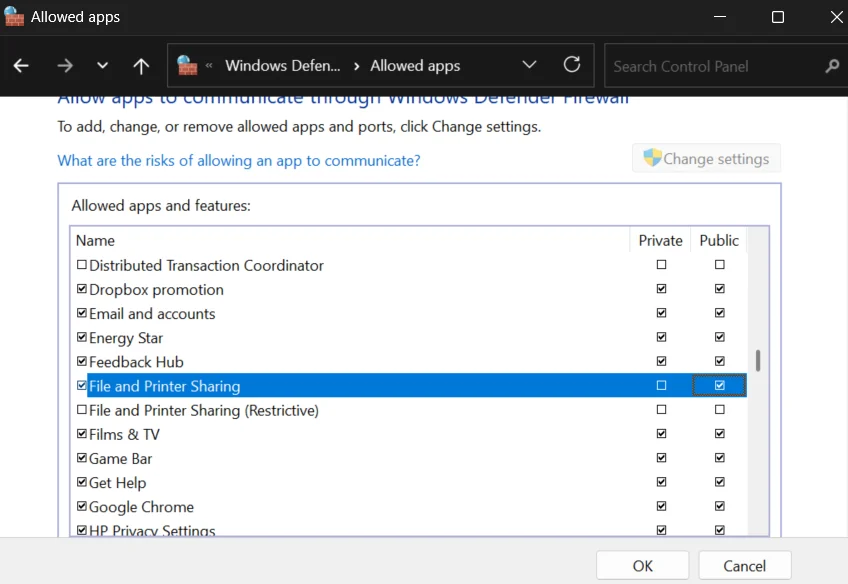
- In the list, tick the Public box next to the File and Printer Sharing option

- Click OK, then must restart your computer.
Reassign the Drive Letter
This error often appears when the drive letter assigned to a network or local drive conflicts with another one. Changing the drive letter can clear that conflict and allow Windows to connect again.
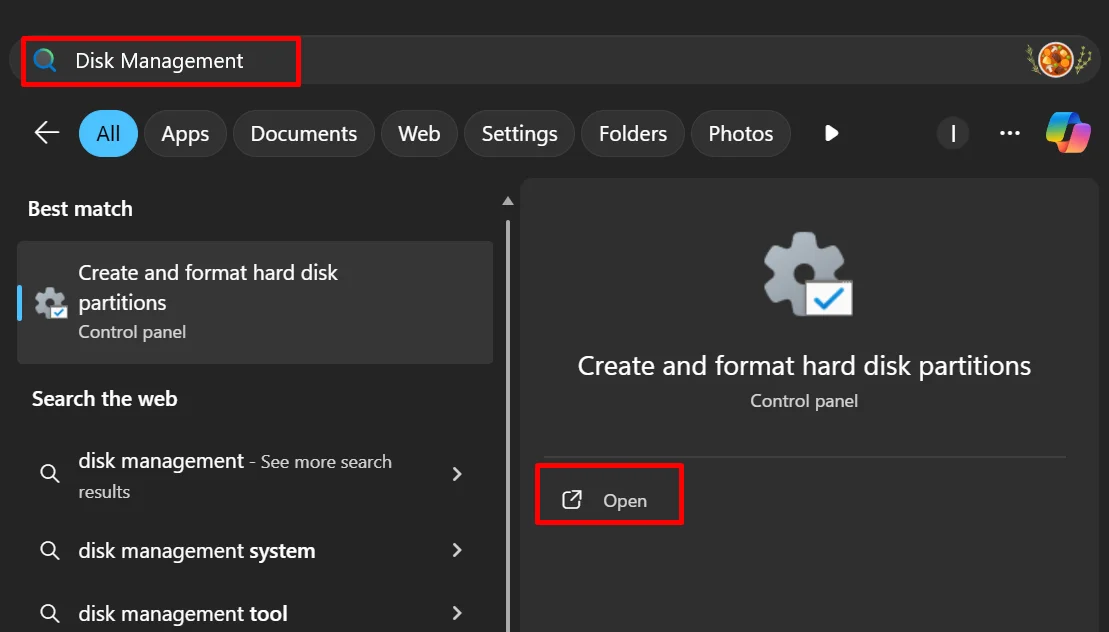
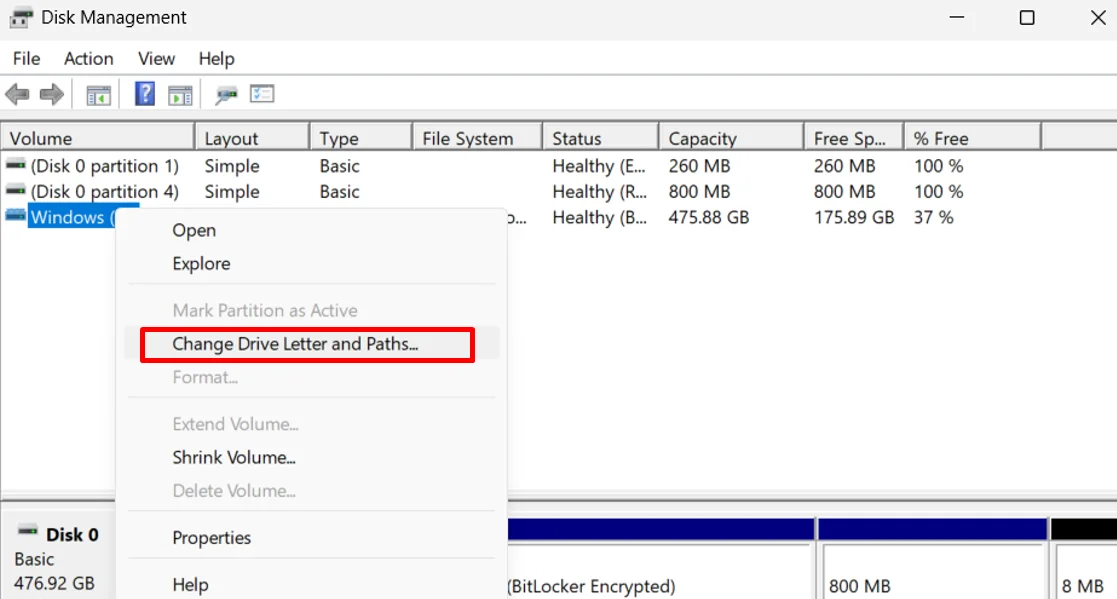
- Press Windows + S, type Disk Management, and open it. (You can also right-click the Start button of Windows and select Disk Management from the menu.)

- In the next window, locate the drive or partition you want to update, then right-click on it.

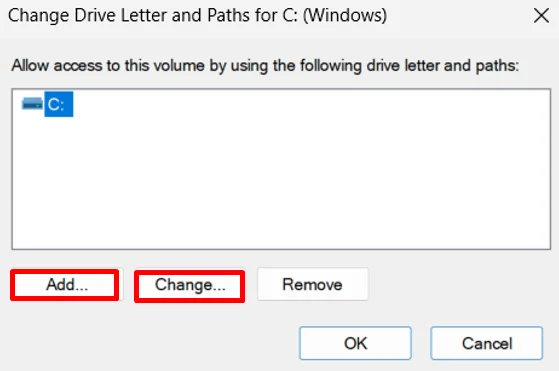
- Choose Change Drive Letter and Paths, then click Add.

Select Assign the following drive letter, open the drop-down list, and choose a new letter.
If the letter you want does not appear, it may already be used by another drive or linked to a removable device that is not plugged in right now. It is also best to avoid using the A and B letters, since they are usually reserved for older systems.
Delete the MountPoints Registry Key
If the error still shows up, try clearing the MountPoints2 entry from the Windows Registry using below steps.
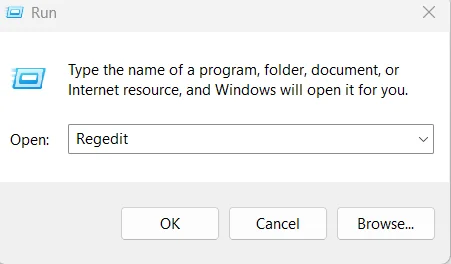
- Press Windows + R to open the Run box.
- Type regedit and press Enter. If a permission message appears, allow it.

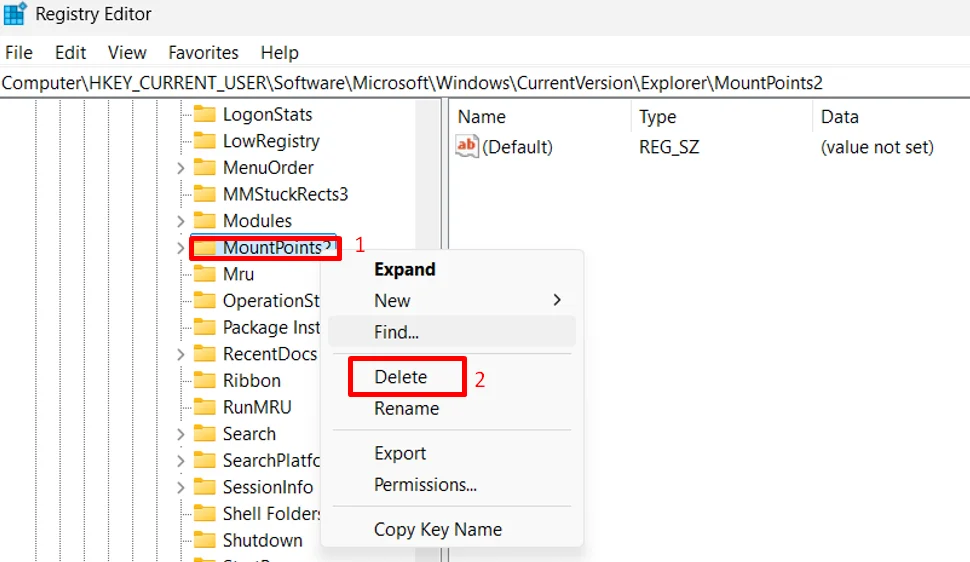
- In the Registry Editor, go to the following location Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer
- Under the Explorer folder, right-click on MountPoints2 and choose Delete.

- After deleting the key, close the Registry Editor and restart your computer then check.
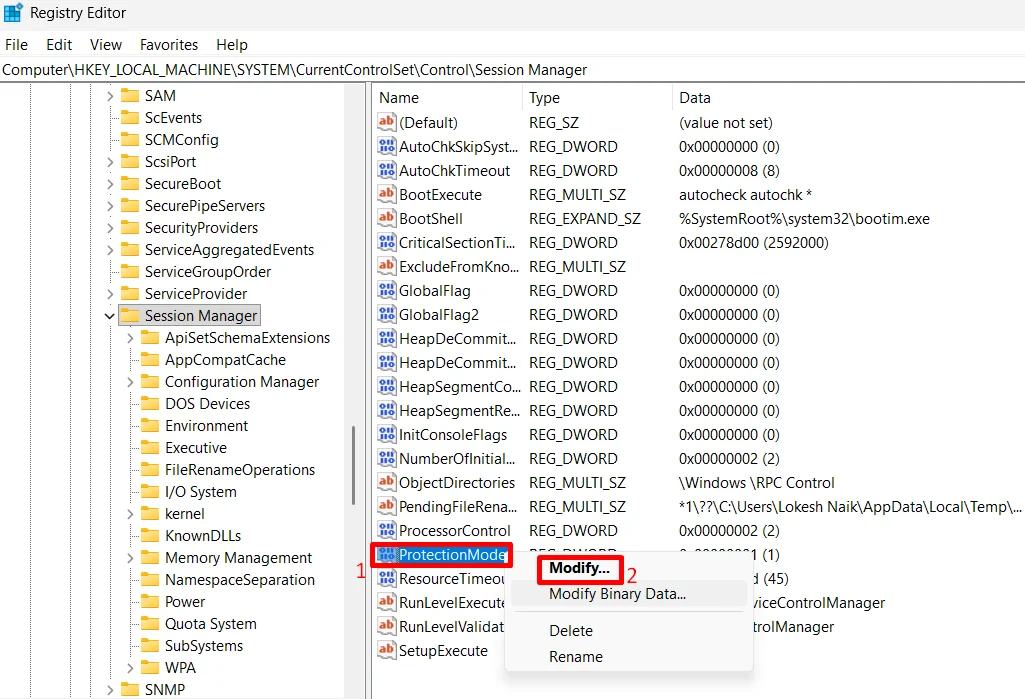
Change the ProtectionMode Value in Registry
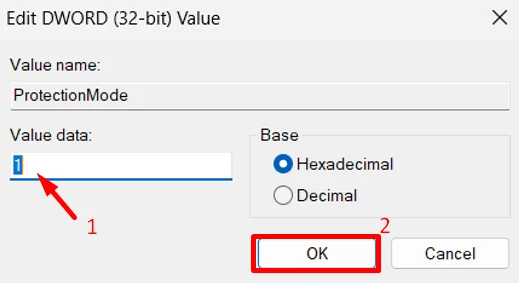
You can also fix this error by updating a setting inside the Windows Registry called ProtectionMode by changing the value so that Windows can handle network connections in a different way.
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type regedit and press Enter. Allow access if a prompt appears
- In Registry Editor, go to the following path HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager
- On the right side, right-click on ProtectionMode, then choose Modify.

- Set the value to 1 and click OK to save the change.

- Close the Registry Editor, restart your computer, and then check if the network drive connects without showing the error.
Check for Windows Updates
Using an older version of Windows can sometimes cause network drive issues like this one. Bugs in the system or missing fixes may stop Windows from connecting to shared drives correctly, so keeping your system up to date is important.
- Press Windows + I to open Settings.
- Click Windows Update from the left side, then select Check for updates.
- If updates are found, click Install now and wait for the process to finish.
Check and Disable VPN Interference
In many cases, a VPN can interfere with network drive connections. When a VPN starts automatically during system boot, it may change how Windows routes network traffic. This can cause the mapped drive path to become unreachable, which then triggers the “local device name is already in use” error.
VPN software often creates a virtual network adapter and assigns new routes or DNS settings. As a result, Windows may try to access the network drive through the VPN tunnel instead of the local network where the file server exists. This can prevent the drive from reconnecting, even though the path and credentials are correct.
To test this, temporarily disconnect or disable the VPN and then try accessing the mapped network drive again.
Adjust Group Policy Settings on a Work Network
On company-owned computers, drive mappings are often controlled by Group Policy. In some cases, these policies may automatically map drives in a way that conflicts with your manual settings, which can trigger this error.
- Open the Run dialog and type gpedit.msc, then press Enter.
- Go to User Configuration > Preferences > Windows Settings > Drive Maps.
Now, look for any drive mappings that conflict with the one causing the issue and remove or edit them as needed. Make sure the Reconnect option is disabled if the drive is not meant to reconnect every time. After making changes, open Command Prompt and run gpupdate /force to apply the updated policy settings.
Use PowerShell to Automate the Fix
If you are tired of fixing mapped drives manually, PowerShell can handle it for you in one step. You can create a small script that clears old network drive mappings and recreates the correct one each time it runs.
Create a file named fix-drives.ps1 and add the following lines to it
net use * /delete /y
New-PSDrive -Name “Z” -PSProvider FileSystem -Root “\\server\share” -Persist
Run this script as an administrator whenever the issue appears, or schedule it through Task Scheduler to run automatically. Just update the drive letter and network path to match your setup.
Free Up Space on the Network Server
In some cases, this error is linked to low storage on the network server itself. When the server does not have enough free space on its main drive, Windows may fail to connect to shared folders and show this message. So, check the available disk space on the server and remove unused files or move data to another location if needed.
- ALSO READ: How To Fix MSCOMCTL.OCX Error in Windows?
Hope this guide helped you fix the local device name is already in use error on your Windows system, whether you are using Windows 7, 8, 10, or 11. If you found another method that worked for you or noticed anything we missed, feel free to share it in the comments so it can help others as well.